A Complete Overview for Website Encryption – SSL Certificates

A Comprehensive Guide to Secure Website Encryption
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security technology that establishes an encrypted connection between a web server and a user’s web browser. It ensures that the data transmitted between the two remains secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with by unauthorized individuals. Here’s some essential information about SSL –
1. SSL Certificate: An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that validates the authenticity of a website and enables secure communication. A trusted Certificate Authority (CA) issues it and contains the website’s public key, information about the issuer, and the website owner’s identity.
2. Encryption: SSL uses encryption algorithms to scramble data transmitted between a web server and a browser, making it unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept it. This protects sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data, from hackers’ access.
3. HTTPS: When an SSL certificate is installed on a website, the URL changes from “http://” to “https://”. The “s” in “https” indicates that the website is secured with SSL encryption. Browsers also display a padlock icon or a green address bar to indicate a secure connection.
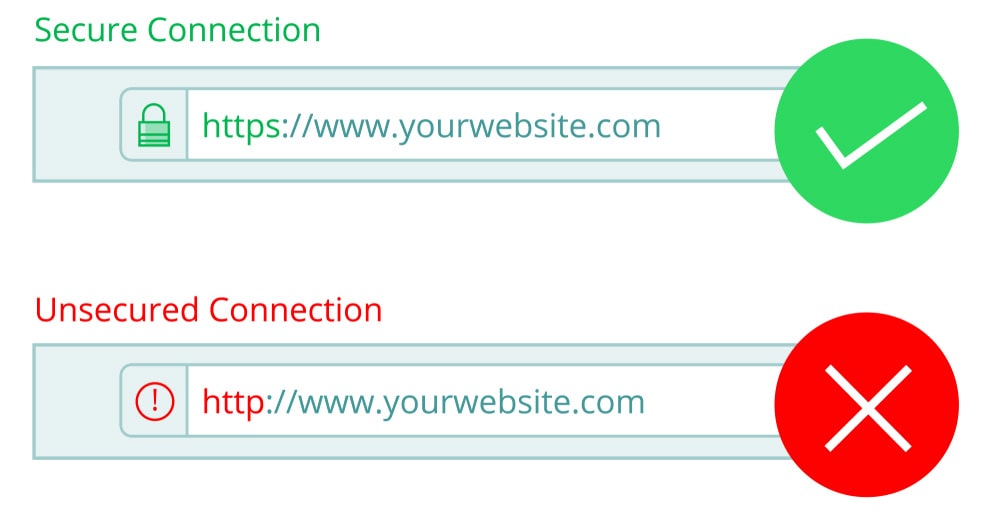
4. Trust and Security: SSL certificates establish website trust and credibility. Visitors are likelier to trust and engage with a website with the secure padlock symbol or the “https” prefix. SSL also protects against phishing attacks and data breaches, enhancing the security of online transactions and user interactions.
5. Certificate Authorities (CAs): SSL certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities. Well-known CAs include Comodo, Symantec, Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, and GlobalSign. It’s essential to choose a reputable CA when obtaining an SSL certificate.
6. SSL Renewal: SSL certificates have an expiration date. It is crucial to renew certificates before expiration to maintain uninterrupted, secure connections. Many certificate authorities offer automatic renewal options to simplify the process.
Implementing SSL on a website is essential for protecting user data, establishing trust, and ensuring secure online communication. Many hosting providers and certificate authorities offer SSL certificates, and the process of obtaining and installing an SSL certificate can vary. It’s recommended to consult with your hosting provider or a trusted SSL certificate provider for specific instructions based on your website’s setup and requirements.
Types of SSL Certificates
Several types of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are available, each offering different levels of validation and security. Here are the main types:
a. Domain Validated (DV) Certificates: DV certificates provide the lowest level of validation and are typically the most affordable option. They verify only the ownership of the domain, ensuring that the certificate holder has control over the domain in question. DV certificates are issued quickly and are suitable for personal websites, blogs, or small businesses where basic encryption is required.
b. Organization Validated (OV) Certificates: OV certificates offer a higher level of validation. In addition to verifying domain ownership, the Certificate Authority (CA) validates the organization’s details, including its legal existence and physical address. OV certificates provide more trust and assurance to website visitors and are suitable for businesses and organizations that require enhanced credibility.
c. Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: EV certificates offer the highest level of validation and provide the most visible trust indicators. The CA conducts a rigorous verification process to confirm the legal and physical existence of the organization. Websites with EV certificates display the organization’s name prominently in the browser’s address bar, often turning it green. EV certificates are recommended for e-commerce websites, financial institutions, and other entities that handle sensitive customer information.
d. Wildcard Certificates: Wildcard certificates secure a domain and all its subdomains with a single certificate. For example, a wildcard certificate for “*.example.com” would secure “blog.example.com,” “shop.example.com,” etc. This simplifies the certificate management process for websites with multiple subdomains.
e. Multi-Domain Certificates (MDC)/Subject Alternative Name (SAN) Certificates: MDC or SAN certificates allow you to secure multiple domain names with a single certificate. This is useful for organizations that manage several websites or have different domain name variations.
f. Single-Page Certificates: Single-page certificates, also known as Single-Domain certificates, are specifically designed for securing a single web page rather than an entire domain. They are helpful for landing pages, microsites, or specific web applications that don’t require a full domain certificate.
When selecting an SSL certificate, consider the level of validation and security required for your website, the number of domains or subdomains you need to secure, and your budget. Choosing a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) is recommended to ensure that your SSL certificate is recognized and trusted by web browsers and visitors.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) benefits
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) provides several benefits for websites and online communication
1. Data Encryption: SSL encrypts the data transmitted between a web server and a user’s browser, making it unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept it. This protects sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data from hackers.
2. Data Integrity: SSL ensures that the data transferred between the server and browser remains intact and unaltered during transit. It detects and prevents any unauthorized modification or tampering with the data.
3. Authentication: SSL certificates validate the authenticity of a website, confirming that it belongs to a legitimate entity. This helps establish trust with visitors, as they can verify the website owner’s identity and ensure they are communicating with the intended server.
4. Trust and Credibility: Websites with SSL encryption display trust indicators such as a padlock icon and “https://” in the browser’s address bar. These visual cues reassure visitors that the website is secure and their data is protected. SSL enhances the credibility of a website and increases user trust, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
5. Protection against Phishing Attacks: SSL protects against phishing attacks by ensuring that users interact with the authentic website rather than fraud. Phishing attackers often attempt to mimic legitimate websites to deceive users and steal their sensitive information. SSL certificates help users identify genuine websites and reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing scams.
6. SEO Benefits: Search engines like Google consider SSL a ranking factor. Websites with SSL encryption boost in search engine rankings compared to non-secure websites. An SSL certificate can improve your website’s visibility and increase organic traffic.
7. Compliance with Data Protection Regulations: SSL encryption is often required to comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). If your website handles personal data or engages in e-commerce transactions, SSL helps ensure compliance with these regulations and protects the privacy of your users.
By implementing SSL on your website, you create a secure and trusted environment for your users, protect their sensitive data, and enhance your online presence. SSL is essential for any website that deals with user information or conducts online transactions, as it establishes a secure connection and safeguards against potential threats.



